Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista Técnica de la Facultad de Ingeniería Universidad del Zulia
versión impresa ISSN 0254-0770
Rev. Téc. Ing. Univ. Zulia v.28 n.2 Maracaibo ago. 2005
Kober fractional q-integral operator of the basic analogue of the H-function
R.K. Saxena1, R.K. Yadav1, S.D. Purohit1 and S.L. Kalla2
1Department of Mathematics & Statistics, Jai Narain Vyas University, Jodhpur-342001, INDIA. 2Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, P. O. Box 5969, Safat 13060 KUWAIT. E-mail: kalla@mcs.sci.kuniv.edu.kw; shyamkalla@yahoo.com
Abstract
This paper deals with the derivation of the Kober fractional q-integral operator of the basic analogue of the H-function defined by Saxena, Modi and Kalla [Rev. Téc. Ing., Univ. Zulia. 6(1983), 139-143]. Several interesting results involving Gq(.);Eq(.); the basic elementary functions and the basic Bessel functions such as Jv(x; q); Yv(x; q); Kv(x; q); Hv(x; q), are deduced as the special cases of the main results.
Key words: Kober fractional q-integral operator, basic integration, basic analogue of Fox’s H-function, basic Bessel functions.
Operador q-integral fraccional Kober de la análoga básica de la función H
Resumen
Este trabajo trata de la derivación del operador q-integral fraccional de Kober de la análoga básica de la función H definida por Saxena, Modi y Kalla [Rev. Téc. Ing., Univ. Zulia, 6 (1983), 139-143. Se deducen varios resultados interesantes que involucran Gq (.); Eq (.); las funciones elementales básicas y las funciones de Bessel básicas tales como Jv(x; q); Yv(x; q); Kv(x; q); Hv(x; q), como casos especiales de los resultados principales.
Palabras clave: Operador q-integral fraccional Kober, integración básica, análoga básica de la función H de Fox, funciones de Bessel básicas.
Recibido el 23 de Septiembre 2004
En forma revisada el 20 de Junio 2005
1. Introduction
A basic analogue of the Kober fractional integral operator, as defined by Agarwal [1], is given as:
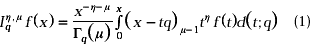
where µ is an arbitrary order of integration with Re(µ)> 0 and h being real or complex.
Following Agarwal [1] and Al-Salam [2], the basic integration is defined as:
![]()
By virtue of the result (2), (1) can be expressed as:
![]()
where Re(µ) > 0 and h being real or complex.
Further, for real or complex a and 0 < |q | < 1, the q-shifted factorial is defined as:
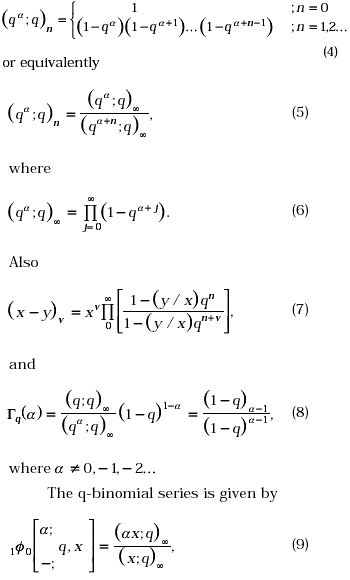
Following Saxena, Modi and Kalla [3], the basic analogue of H-function is defined as:
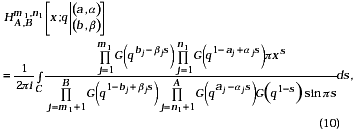
where 0 ≤ m1 ≤ B, 0 ≤ n1 ≤ A; a'i s and b'j s are all positive integers, the contour C is a line parallel to Re(ws)= 0, with indentations, if necessary, in such a manner that all poles of, G(qbj-bjs),1≤ j ≤ m1 are to the right, and those of G(q1-aj+ajs),1≤ j ≤ n1, to the left of C. The integral converges if Re[s log(x) - log sin ps] < 0 for large values of |s| on the contour, that is, if |{arg(x) - w2w1-1 log|x|}| < p, where 0 < |q | < 1, log q = -w = -(w1 + iw2), w, w1, w2 are definite quantities, w1 and w2 being real.
Further, the q-gamma’s used above are given by
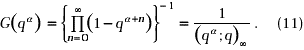
Indeed, it is interesting to observe that
(q;q)∞(1-q)1-aG(qa) = Gq(a). (12)
If we set ai = bj = 1,"i and j in equation (10), then it reduces to the basic Meijer’s G-function, namely
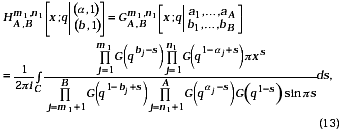
where 0 ≤ m1 ≤ B, 0 ≤ n1 ≤ A and Re[s log(x) - log sin ps] < 0. For the shortened notation, the basic analogue of the G-function will be denoted by Gq(.). Further, if we take n1 = 0; m1= B in (13), we arrive at the following basic analogue of MacRobert’s E-function
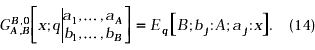
The basic analogues of the Bessel functions Ju(x), Yu(x), Ku(X), Hu(x); which are expressible in terms of the function Gq(.) cf. Saxena and Kumar [4], are defined as:
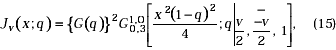
where Ju(x;q) denotes the q-analogue of Bessel function Ju(x).
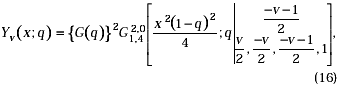
where Yu(x;q) denotes the q-analogue of the Bessel function Yu(x).
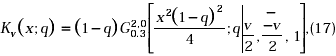
where Ku(X;q) denotes the basic analogue of the Bessel function of the third kind Ku(X).
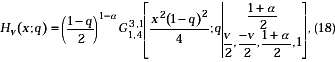
where Hu(x;q) is the basic analogue of the Struve function Hu(x).
By virtue of the definition (13), the following elementary basic (q-) functions are expressible in terms of the basic analogue of Meijer’s G-function as:

A detailed account of various special functions expressible in terms of Meijer’s G-function [5] or Fox’s H-function can be found in research monographs by Mathai and Saxena [6, 7].
The object of this paper is to evaluate Kober fractional basic integral operator of the basic analogue of the H-function and then to deduce certain results involving Gq(.), Eq(.), various basic Bessel and q-elementary functions as applications of the main result. The results obtained in this paper are believed to be a new contribution to the theory of q-fractional calculus and are likely to find certain applications to the solution of the fractional q-integral equations involving various q-hypergeometric functions. In this connection one can refer to the work of Prabhakar and Chakrabarty [8], and Yadav and Purohit [9].
2. Main Results
In this section, we will evaluate the following fractional q-integral operator of Kober type involving basic analogue of the H-function.

Proof: Using (3) and (10) the left hand side of (24) can be expressed as:

On interchanging the order of summation and integration, which is valid under conditions given with (24), we obtain
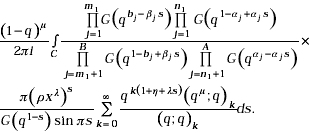
On summing the inner 1f0(.) series with the help of equation (9) and then making use of the relation (5), it yields
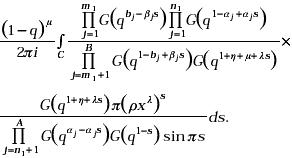
The above expression on being interpreted with the help of (10), yields the right hand side of (24).
Similarly, we can prove (25).
3. Applications
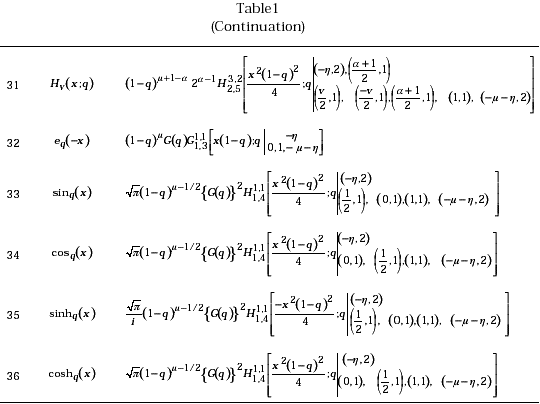
In this section, we will deduce the following eleven results given in tabular form, as applications, of the general result (24).
The results (26) and (27) follows directly from (24) in view of the definitions (13) and (14) respectively. Where as the results (28)-(31) can be obtained by taking ![]() and l = 2 in (24) and make use of the results (15)-(18). Similarly, one can prove the results (32)-(36) by suitably assigning values to the parameters in light of the definitions (19)-(23). It is further interesting to observe that for h= 0, and on employing the relation
and l = 2 in (24) and make use of the results (15)-(18). Similarly, one can prove the results (32)-(36) by suitably assigning values to the parameters in light of the definitions (19)-(23). It is further interesting to observe that for h= 0, and on employing the relation
![]()
one can obtain several special cases, where ![]() denotes the Riemann-Liouville fractional q-integral operator, given by
denotes the Riemann-Liouville fractional q-integral operator, given by
![]()

Acknowledgement
The third author (S. D. Purohit) is grateful to CSIR, Govt. of INDIA, for providing a Junior Research Fellowship No. 9/98(51)2003-EMR-I, to enable him to carry out the present investigations. The authors are also thankful to the referee for his valuable comments and suggestions.
References
1. Agarwal, R.P.: Certain fractional q-integrals and q-derivatives. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 66 (1969), 365-370. [ Links ]
2. Al-Salam, W.A.: Some fractional q-integrals and q-derivatives. Proc. Edin. Math. Soc. 15 (1966), 135-140. [ Links ]
3. Saxena, R.K., Modi, G.C. and Kalla, S.L.: A basic analogue of Fox’s H-function. Rev. Tec. Ing., Univ. Zulia 6 (1983), 139-143. [ Links ]
4. Saxena, R.K. and Kumar, R.: Recurrence relations for the basic analogue of the H-function. J. Nat. Acad. Math. 8 (1990), 48-54. [ Links ]
5. Erdélyi, A. and Magnus, W., Oberhettinger, F. and Tricomi, F.G.: Tables of Integral Transforms. Vol-II, McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc., New York, 1954. [ Links ]
6. Mathai, A.M. and Saxena, R.K.: Generalized Hypergeometric Functions with Applications in Statistics and Physical Sciences. Lecture Series in Math. No.348, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 1973. [ Links ]
7. Mathai, A.M. and Saxena, R.K.: The H-function with Applications in Statistics and other Disciplines. John Wiley & Sons. Inc. New York, 1978. [ Links ]
8. Prabhakar, T.R. and Chakrabarty, M.: A class of basic integral equations with basic hypergeometric function 1f1(.) in the kernels. Indian J. Pure. Appl. Math. 7(1976), 1253-1260. [ Links ]
9. Yadav, R.K. and Purohit, S.D.: Application of Riemann-Liouville fractional q-integral operator to basic hypergeometric functions. Acta Ciencia Indica 30(iii)(2004), 593-600. [ Links ]
10. Gasper, G. and Rahman, M.: Basic Hypergeometric Series. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990. [ Links ]













