Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Revista Latinoamericana de Metalurgia y Materiales
Print version ISSN 0255-6952
Rev. LatinAm. Metal. Mater. vol.34 no.2 Caracas June 2014
CARACTERIZACIÃN ESTRUCTURAL Y ESTABILIDAD DE LAS FASES PARA PELÃCULAS DE Ti6Al4V DEPOSITADAS POR MEDIO DE PULVERIZACIÃN CATÃDICA MAGNETRÃN RF SOBRE ACERO INOXIDABLE [ Links ]
1* 12
Carlos M. Garzón, J. Edgar Alfonso, Edna C. Corredor
1: Departamento de FÃsica, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Ciudad Universitaria, Bogotá, Colombia.
2: Facultad de IngenierÃa, Universidad Libre de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia.
*e-mail: cmgarzono@unal.edu.co
RESUMEN
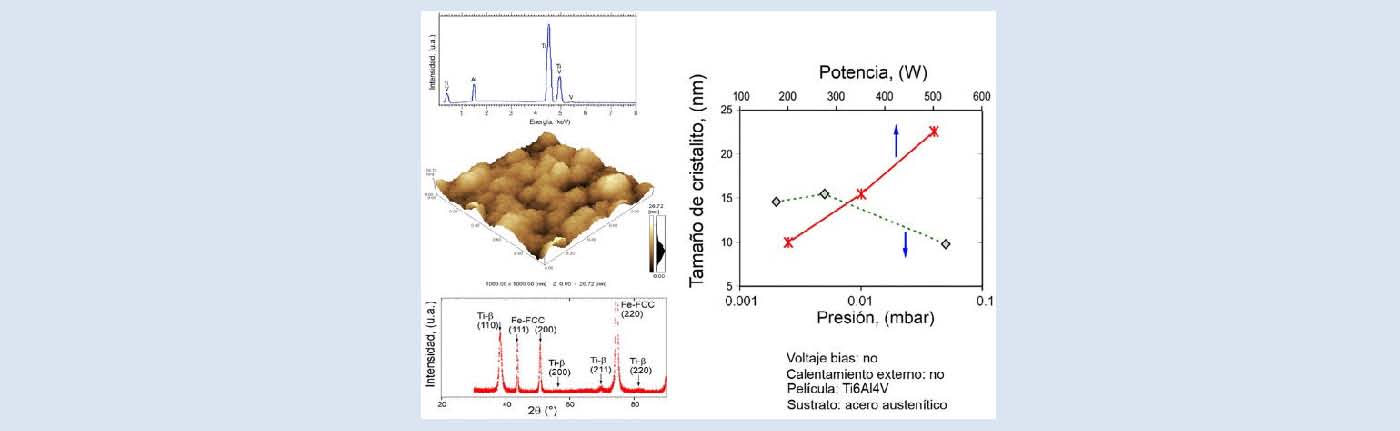
El acero inoxidable UNS S31600 fue recubierto con pelÃculas de la aleación Ti6Al4V, por medio de la técnica de pulverización catódica magnetrón rf. La superficie de los materiales obtenidos se sometió a una caracterización estructural por difracción de rayos X y a análisis quÃmico por espectrometrÃa de energÃa dispersiva de rayos X. Se estudió el efecto de las variaciones de la presión del gas en la cámara de crecimiento y de la potencia aplicada al blanco sobre la estabilidad de las fases y el tamaño de cristal. Se obtuvieron pelÃculas nanoestructuradas, constituidas de la fase Ti-cúbica de cuerpo centrado altamente texturadas. La textura y la composición quÃmica de las pelÃculas sufrieron poca alteración al variar los parámetros del proceso de recubrimiento, mientras que el tamaño de cristal mostró ser bastante susceptible a las variaciones en dichos parámetros. Utilizando análisis de Scherrer se estimó que el tamaño promedio de cristal osciló entre 10 y 30 nm. El uso de potencias menores y de presiones mayores en los experimentos llevó a la formación de cristales más finos. El artÃculo discute los fundamentos fÃsicos que controlan la formación de las fases observadas y su tamaño de cristal.
Palabras Claves: PelÃculas delgadas, Nanoestructuras, Biomateriales, Pulverización catódica magnetrón rf, Difracción de rayos X.
STRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND NEW INSIGHTS INTO PHASE STABILITY OF Ti6Al4V FILMS MAGNETRON SPUTTER GROWN ONTO A STAINLESS STEEL
ABSTRACT
Ti6Al4V films were grown onto an UNS S31600 austenitic stainless steel by rf magnetron sputtering. Sample surfaces were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, aiming to characterize film structure, and by energy dispersive spectroscopy, for chemical composition determination. Deposition experiments varying both chamber pressure and plasma power were carried out. The effect of those variations in pressure and power on type of phases formed and their crystal size was appraised. Ti-BCC films with sharp texture and nanometric sized crystals were obtained. Film preferred crystallographic orientation and chemical composition were almost unaffected by variations on both pressure and power. On the other hand, crystal size was highly dependent on deposition parameters. Scherrer's analysis allowed estimating average crystal sizes which ranged between 10 and 30 nm approximately. Lower plasma powers or higher chamber pressures led to smaller film crystals. The role of physical parameters controlling stability of crystal phases and their crystal size is discussed.
Keywords: Thin films, Nanostructures, Biomaterials, rf-Magnetron sputtering, X-ray diffraction.
Recibido: 02-03-2013 ; Revisado: 02-11-2013
Aceptado: 06-12-2013 ; Publicado: 12-16-2013













